e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 14 > Part 4 > Year 2020 > Page 601 > Vitaceae > Causonis
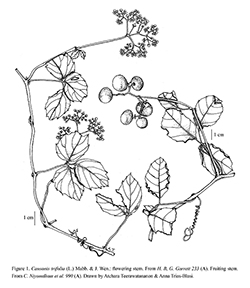
2. Causonis trifolia (L.) Mabb. & J.Wenwfo-0001429016
in Mabberley, Pl.-Book, ed. 4: 1101. 2017; J.Wen, L.M.Lu & Boggan, Philipp. J. Sci. 142: 235. 2013.— Vitis trifolia L., Sp. Pl. 1: 203. 1753; King, J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal, Pt. 2, Nat. Hist. 65: 402. 1896.— Cissus trifolia (L.) K.Schum. in K.Schum. & Hollrung, Fl. Kais. Wilh. Land 71. 1889.— Cayratia trifolia (L.) Domin, Biblioth. Bot. 89: 370. 1927; Suess., Nat. Pflanzenfam. 20d: 280. 1953; Backer & Bakh.f., Fl. Java (Spermatoph.) 2: 93. 1965; Momiy. In H.Hara, Fl. E. Himalaya 1: 199. 1966; Momiy. In H.Hara & L.H.J.Williams, Enum. Fl. Pl. Nepal 2: 94. 1979; Latiff, Sains Malaysiana, 10(2): 135; Jackes, Austrobaileya 2(4): 368. 1987; C.L.Li, Fl. Reipubl. Popularis Sin. 48(2): 75. 1998; B.V.Shetty & P.Singh, Fl. Ind. 5: 275. 2000, Ren & J.Wen, Fl. China 12: 191. 2007; W.J.Kress et al., Contr. U.S. Natl. Herb. 45: 393. 2003; Trias-Blasi, Fl. Nepal Vitaceae: Webedition 1. 2017. Fig. 1. Plate LXVII: C–D.
Accepted Name : This is currently accepted.
Synonyms & Citations :
Description : Herbaceous climber. Stem cylindrical, 2–4 mm diam., profusely branched, hairy with pale bent hairs 0.2–1 mm long to glabrous, slightly ridged; tendrils 2–5-furcate, slender, wiry, leaf-opposed, cylindrical, peduncle 1–4 cm long, then bifurcating and coiling 1.5–7 cm long, sparsely hairy. Leaves trifoliolate; petiole 10–60 by 1–1.75 mm, hairy as stem, central petiolule 0.5–2.5 cm long, lateral petiolules 2–8 mm long, hairy as stem; blade of central leaflet oval to subovate, 2–10 by 1–7 cm, base cuneate to rounded; blade of lateral leaflet 2.5–7 by 2–6 cm, base oblique; margin dentate with teeth to 0.5 by 0.8 mm to sinuate, apex acute, adaxial surface almost glabrous except for hairs (like those on stem) on midrib to densely hairy with appressed hairs, abaxial side moderately to densely hairy with hairs like those on stem, mostly concentrated on veins, veins protruding, 1 main basal vein, 4–8 pairs of secondary veins. Inflorescence ramified, axillary, mostly dividing dichotomously, lax, 2–12 cm long; peduncle 15–80 by 1–1.5 mm, hairy as stem, pedicel 1–3 mm long, hairy with hairs to 0.1–0.2 mm long. Buds ovoid, 1.5–2 by 1–2 mm. Calyx cupuliform, entire, margin sinuate, 0.5–0.75 by 1.5–2 mm, hairy as in pedicel. Petals 4, ovate, 2–2.25 by 1–1.5 mm, apex cucullate, sparsely to densely puberulent. Stamens 4; filaments flattened, broadening at base, 0.75–1 mm long; anthers orbicular, medifixed, 0.4–0.75 mm long. Disc with 4 distinct lobes, 0.5–1 by 1.5 mm, glabrous. Style slender, 0.5–0.6 mm long; stigma inconspicuous. Fruit subglobose, 5–15 mm diam., glabrous, smooth, base attenuate. Seeds 2–4, triangular, 5–6 by 4.5–5 mm, adaxial side with two faces, abaxial side convex with a linear chalazal knot, side ribbed.
Thailand : NORTHERN: Chiang Mai (Bo Luang, Chiang Mai, Doi Muang On), Chiang Rai, Lampang (Doi Luang), Nakhon Sawan; NORTH-EASTERN: Loei (Wang Saphung), Khon Kaen (Phu Khiao); EASTERN: Nakhon Ratchasima (Khao Khiao), Buri Ram (Sateuk); SOUTH-WESTERN: Kanchanaburi (Khiti, Wangka), Phetchaburi (Kaeng Krachan), Prachuap Khiri Khan (Bang Saphan); CENTRAL: Saraburi (Sam Lan), Krung Thep Maha Nakhon (Bangkok); SOUTH-EASTERN: Chon Buri (Si Chang Island); PENINSULAR: Surat Thani (Donsak, Ko Tao), Nakhon Si Thammarat (Khao Luang), Songkhla (Songkla Lake), Narathiwat (Bang Khun Thong, Bang Nara).
Distribution : India (neotype of Causonis trifolia, lectotype of C. carnosa), Nepal, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Myanmar, China, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Australia.
Ecology : Dry dipterocarp forests, disturbed areas, 0–900 m alt. Flowering: February–September; fruiting: May–December.
Vernacular : Khruea phat sam (เครือพัดสาม)(Northern); thao khan (เถาคัน)(Narathiwat); thao khan daeng (เถาคันแดง)(Central).
Uses: The root is astringent. Ground with black pepper, it is applied as poultice on boils. A poultice of leaves is applied to ulcers and yoke-sores of bullocks. Fermentation with a hot decoction of the roots or leaves is said to cause perspiration in case of high fever (Shetty & Singh, 2000). The sap can be drunk (Gagnepain, 1912).