e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 9 > Part 4 > Year 2008 > Page 423 > Cucurbitaceae > Coccinia
Coccinia grandis (L.) Voigtwfo-0000612919
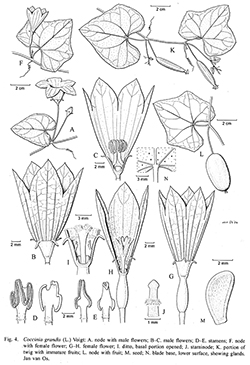
Hort. Suburb. Calcutt. 59. 1845; Backer in Backer & Bakh. f., Fl. Java 1: 305. 1964; Keraudren in Aubrév. & J.-F.Leroy, Fl. Cambodge, Laos & Vietnam 15: 66, pl. 11: 1–3. 1975; 176; P.H.Hô, Câyco Vietnam 1, 2: 727, f. 2018. 1991; PROSEA 8: 150. 1993; S.K.Chen in C.Y.Wu, C.Chen & S.K.Chen, Fl. Yunnan. 6: 383, pl. 101: 1–3, 6. 1995.— Bryonia grandis L., Mant. Pl.: 126. 1767. Fig. 4.
Accepted Name : This is currently accepted.
Synonyms & Citations :
Description : Climber to 8 m long, sparsely puberulous, early glabrescent; older stem to 15 mm across, with grey bark. Probract fleshy, elliptic to oblong, 2–3 mm long, caducous. Tendrils unbranched. Leaves: blade slightly succulent, 3–10 cm across, unlobed, (3- or) 5-angular or - lobed, or deeply 3–5(–7-)lobed, or dissected to ⅘ deep, the lobes short to oblong, with apex acute or rounded, glands small, several, near insertion of petiole and along lateral veins, cystoliths in older leaves present, base deeply cordate, margin minutely (blackish) dentate sinuate; petiole 1–2.5 cm long. Male flowers solitary (or 2 or 3); pedicel 20–50 mm long; receptacle-tube cup-shaped, narrowed to the base, 6–8 mm long, ca 6 mm wide at throat, greenish white; sepals oblong-subulate, ca 3 mm long, ± up-curved, pale green; corolla white (pale green veined), broad-campanulate, (15–)25–30 mm long, the lower (½–)⅔ fused, lobes ovate-oblong, acute(-acuminate), inside (sparsely) pubescent; stamens inserted ca 5 mm below the receptacle-throat; filaments either connate or free but coherent, forming a seemingly solid but hollow column (4–)5–6 mm long (sometimes leaving 3 openings at base); anthers two 2-thecous, one 1-thecous, free, but mostly coherent into a subglobose whole, ca 5 mm diam.; the receptacle-tube below the insertion of the stamens densely white-hairy, hiding a basal hollow, ca 3 mm deep, comprising a conspicuous green-yellow cup-shaped disc adnate to the bottom of the tube. Female flowers resembling male flowers, solitary; pedicel 1–3 cm long; ovary oblong, narrowed at both ends, 10(–13) by 2–3) mm; style 3–5 mm long, at base surrounded by a cup-shaped disc; stigmas 3, broad, oblong, 5–7 mm long, papillose; staminodes 3, minute. Fruit pendent, ellipsoid or oblong, 2.5–6 by 1.5–3 cm, apex subacute, green-white blotched, ripening red (starting at the apex), pulp juicy, red; fruiting pedicel 1–4 cm long. Seeds 6–7 by 2.5–3 by ca 1.5 mm, ± smooth, whitish, margin narrow.
Thailand : Common throughout Thailand, but no collections seen from North-Eastern and Eastern region.
Distribution : Widely distributed in the Old World, northern tropical Africa, east to Arabia through India (type) to Malesia and tropical N Australia.
Ecology : Prefers a (strong to) light monsoon climate. Common in open forests, scrub, along waste land, and roadsides, 0–400 m alt. Flowering and fruiting throughout the year.
Vernacular : Khae-do (แคเด๊าะ)(Karen-Mae Hong Son); phak khaep (ผักแคบ)(Northern); phak tamlueng (ผักตำลึง)(Central).
Uses: Young shoots are eaten as a vegetable.
Notes: Fruits are (glaucous) green with contrasting white blotches in rows and turn into bright red when ripe, except for the very base. The pulp is frequently eaten by animals, mainly by birds.