e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 9 > Part 3 > Year 2008 > Page 283 > Fagaceae > Lithocarpus
18. Lithocarpus encleisacarpus (Korth.) A.Camuswfo-0000229905
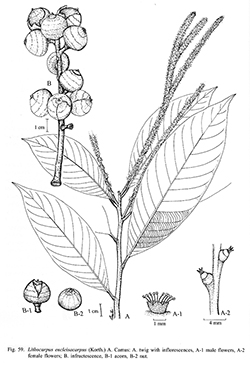
Rivièra Sci. 18: 40. 1932; Barnett, Quer. Rel. Fag. Asia: 144. 1940; Trans. & Proc. Bot. Soc. Edinburgh 34: 335. 1944; Soepadmo, Fl. Males., ser. I, 7: 338. 1972; Soepadmo, S. Julia & R. Go, Tree Fl. Sabah & Sarawak, 3: 56. 2000.— Quercus encleisacarpa Korth, Verh. Nat. Gesch. Ned. Bezitt., Bot.: 209, t. 45. 1844; King ex Hook.f., Fl. Brit. Ind. 5: 617. 1888; Corner, Wayside Trees Mal.: 302, f. 95, 98. 1940.— Cyclobalanus encleisacarpa (Korth.) Oerst., Vidensk. Meddel. Dansk Naturhist. Foren. Kjøbenhavn 8: 81. 1867.— Pasania encleisacarpa (Korth.) Gamble, J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal, Pt. 2, Nat. Hist. 75.2: 449. 1915; Ridl., Fl. Malay Penin. 3: 386. 1924.— Synaedrys encleisacarpa (Korth.) Koidz., Bot. Mag. (Tokyo) 30: 186. 1916.— Castanopsis encleisacarpa (Korth.) Rehder, J. Arnold Arbor. 1: 122. 1919. Fig. 59; Plate XXV: 1.
Accepted Name : This is currently accepted.
Synonyms & Citations :
Description : Tree, 8–25 m high, 80–150 cm girth. Buds ovoid; bracts linear ca 5 by 1 mm, pubescent outside. Twigs glabrous, blackish, sparsely lenticellate. Bark grey, smooth or scaly; inner bark reddish-brown; sapwood yellowish-white. Leaves oblong or elliptic, 7–16 by 3.5–6 cm; base obtuse, slightly cuneate, asymmetrical; apex acute or acuminate, rarely obtuse; margins entire; subcoriaceous to chartaceous, glabrous and glossy green on the upper surface, pubescent then glabrescent and more or less glaucous on the lower; midrib and nerves prominent on the lower surface, depressed on the upper; lateral nerves 8–9 pairs, arched and more or less anastomosing, scalariform veins fine, distinct on the lower surface. Petiole 0.5–1.5 cm, glabrous, blackish when dry. Inflorescences male and female separate or female below, in spikes, axillary or terminal, 5–20 cm long, grey pubescent. Male inflorescence simple or few branched, spike or spikelets 5–20 cm long; bracts and bracteoles ovate, 0.4–0.5 by 0.3–0.5 mm, pubescent outside. Male flowers yellowish, scented, solitary or in 1–3-flowered cluster; calyx 6, ca 1 mm long, lobes divided ca ¼ to the base, pubescent outside; stamens 8–10, 1.5–2 mm long, glabrous; rudimentary ovary subglobose, ca 1 mm in diam., hairy. Female inflorescence spike 8–20 cm long. Female flowers solitary, not in clusters, other characters as in male flowers; styles 3–4, conical, divergent, ca 1.5 mm long; stigmata pointed. Acorns ovoid or turbinate, 2–2.7 cm in diam. (including cupule); fruit stalk 0.5–0.7 cm long on erect and woody infructescence, 15–17 cm long; acorns free, easily dehiscent in irregular parts. Cupule turbinate, base broader than the upper part, completely enclosing the nut except around umbo; wall smooth, densely greenish-brown hairy, conspicuous, 2–3 undulate horizontal filiform lines on the wall only. Nut 1, ovoid to globose, 2–2.5 cm in diam., greyish pubescent.
Thailand : NORTHERN: Chiang Mai; EASTERN: Ubon Ratchathani; SOUTH WESTERN: Kanchanaburi; SOUTH-EASTERN: Chanthaburi; PENINSULAR: Nakhon Si Thammarat, Trang, Satun, Songkhla, Pattani.
Distribution : Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia (Sumatra – type).
Ecology : Tropical evergreen rain forests to lower montane rain forests, pine deciduous dipterocarp forests, often near streams, 50–1,200 m (most commonly 300–800 m). Flowering: April–November (most commonly June–August); fruiting: April–January (most commonly April–July).
Vernacular : Ko fai (ก่อฝ้าย), ko hin (ก่อหิน)(Eastern); ko chaeng (ก่อแจง)(Southeastern); ko hin (ก่อหิน), ko pan (ก่อปัน)(Peninsular).
Uses: Nuts edible.