e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 9 > Part 3 > Year 2008 > Page 239 > Fagaceae > Castanopsis
32. Castanopsis tribuloides (Sm.) A.DC.wfo-0000815457
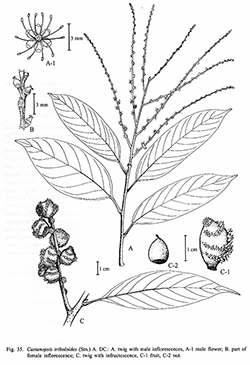
J. Bot. 1: 182. 1863; Prodr. 16.2: 111. 1864; King ex Hook.f., Fl. Brit. Ind. 5: 622. 1888; Brandis, Indian Trees 634. 1921; Hickel & A.Camus, Fl. Indo Chine 5: 1017. 1930; Barnett, Quer. Rel. Fag. Asia: 172. 1940; Trans. & Proc. Bot. Soc. Edinburgh 34: 336. 1944; Hjelmq., Dansk Bot. Ark., 23.4: 498. 1968; C.C.Huang, Y.T.Chang & B.M.Bartol. in C.Y.Wu & P.H.Raven, Fl. China 4: 329. 1999.— Quercus tribuloides Sm., in Rees. Cycl. 29: n. 13. 1814.— Castanea tribuloides (Sm.) Lindl. in Wallich, Pl. Asiat. Rar. 2: 6 1830; Kurz, Forest Fl. Burma 2: 480. 1877. Fig. 35.
Accepted Name : This is currently accepted.
Description : Tree, 6–40 m high, 70–150 cm girth. Terminal buds ovoid, 5–10 by 3–4 mm, pubescent outside. Twigs greyish pubescent, glabrescent. Bark dark brown, rough, with longitudinal irregular fissures 2 cm thick; inner bark reddish; sapwood white. Leaves lanceolate or oblong, 7–21 by 3–6.5 cm; base obtuse, oblique; apex acuminate or acute, sometimes caudate; margins entire; coriaceous to subcoriaceous, glabrous, glossy green on the upper surface, subdepressed on the upper, brownish on the lower; midrib and lateral nerves prominent on the lower surface; lateral nerves 9–13 pairs, arched but not anastomosing; other veins indistinct. Petiole 1–1.8 cm, glabrous, black when dry. Inflorescences male and female mixed or separate, terminal or axillary, pubescent. Male inflorescences always branched, spikelets 5–14 cm long; bracts and bracteoles triangular, ca 1 by 1 mm, pubescent outside. Male flowers whitish to brownish, scented, usually in 2–3-flowered cluster; calyx 6-lobed, lobes free, obovate, 1.5–2 by 1 mm, pubescent on both sides; stamens 12, 2.5–3 mm long, glabrous; rudimentary ovary globose, flat on top, ca 1 mm in diam., hirsute. Female inflorescence spike 8–15 cm long. Female flowers solitary, other characters as in male flowers; styles 3, divergent; stigmata pointed. Fruits ellipsoid, rarely ovoid, 1.5–2.5 by 1.5–2 cm (including cupule), on erect and woody infructescence, 15–20 cm long. Cupule completely enclosing the nut except the umbo, but not fused with it; wall sparsely covered with simple spines which curl in twisted lines from base to apex. Nut 1, ovoid, 1.2–1.5 by 1–1.2 cm, apex conical.
Thailand : NORTHERN: Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Lamphun, Lampang, Tak; NORTH EASTERN: Phetchabun, Loei; EASTERN: Nakhon Rachasima; SOUTH-WESTERN: Kanchanaburi; SOUTH-EASTERN: Prachin Buri, Trat.
Distribution : India, Nepal (type), Burma, China, Laos, Vietnam.
Ecology : Lower montane rain forests, lower montane pine-oak forests, deciduous forests. From summit to gallery on sandstone to granite bedrock, 600–1,700 m (most commonly 1,000–1,300 m). Flowering: January–November (most commonly May–June); fruiting: March–November (most commonly June–September).
Vernacular : Ko khao (ก่อข้าว), ko dueai (ก่อเดือย), ko laem (ก่อแหลม), ko bai lueam (ก่อใบเลื่อม), ko nam (ก่อหนาม), ko duk (ก่อดูก)(Northern); ko nuat maew (ก่อหนวดแมว), ko laem (ก่อแหลม), ko haeng (ก่อแห้ง)(Northeastern).
Uses: Nuts edible, a pioneer species for forest plantations.