e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 9 > Part 3 > Year 2008 > Page 185 > Fagaceae > Castanopsis
1. Castanopsis acuminatissima (Blume) A.DC.wfo-0000812678
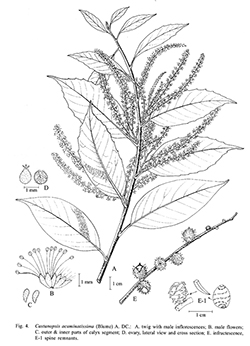
J. Bot. 1: 182. 1863; Hickel & A.Camus, Fl. Indo-Chine 5: 1012. 1930; Barnett, Quer. Rel. Fag. Asia: 162. 1940; Trans. & Proc. Bot. Soc. Edinburgh 34: 336. 1944; Soepadmo, Fl. Males., ser. I, 7: 307. 1972; Soepadmo, Julia & Go, Tree Fl. Sabah & Sarawak, 3: 7. 2000.— Castanea acuminatissima Blume, Mus. Bot. 1: 283. 1850.— Quercus acuminatissima (Blume) A.DC., Prodr. 16.2: 102. 1864; Backer & Bakh.f., Fl. Java 2: 6. 1965.— Pasanea acuminatissima (Blume) Oerst., Vidensk. Meddel. Dansk Naturhist. Foren. Kjøbenhavn 8: 84. 1866; Ridl., Fl. Malay Penin. 3: 386. 1924. Fig. 4; Plate XVII: 1.
Accepted Name : This is currently accepted.
Synonyms & Citations :
Description : Tree, 10–40 m high, 60–250 cm girth. Lateral buds ellipsoid, ca 1 mm long, glabrous. Twigs pubescent then glabrescent, blackish or dark brown when dry. Bark greyish-brown to dark brown, densely lenticellate, flaky and longitudinally fissured; inner bark granular, reddish, brownish or yellow; sapwood yellowish-white. Stipules triangular, 1.5 by 1 mm. Leaves elliptic oblong or oblong-lanceolate, 5.5–13 by 1.5–4 cm; base obtuse to slightly oblique; apex caudate, acuminate or cuspidate; margins serrate in the upper half; subcoriaceous, glabrous, glossy green on the upper surface and pale on the lower; midrib prominent on the lower surface and subdepressed on the upper; lateral nerves 8–11 pairs, conspicuous on both surfaces, scalariform and reticulate veins hardly distinct on either surface. Petiole 1–1.4 cm, pubescent then glabrescent. Inflorescences: male and female separate, rarely mixed, erect, terminal or axillary, pubescent. Male inflorescence much branched or simple, spikelets 8–15 cm long. Male flowers yellowish, solitary, rarely in clusters; bracts and bracteoles triangular, 1.5–2 by 1 mm, pubescent outside; calyx 6-lobed, lobes free, ovate or obovate 1.5–2 by 1 mm, pubescent outside, ciliate; stamens 10–12, glabrous, 2–3 mm long; rudimentary ovary globose, ca 0.5 mm in diam., hirsute. Female inflorescences spike 8–15 cm long. Female flowers as male; styles 3, divergent, stigmata blunt, glabrous. Fruits sessile, globose or ovoid, 1–1.5 by 0.8–1.3 cm (including cupule), on erect infructescence 9–12 cm long. Cupule completely enclosing but not fused with the nut; wall sparsely covered with simple spines, curved beyond their bases, pubescent then glabrescent; dehiscent. Nut 1 per cupule, ovoid, ca 1 cm in diam., glabrous.
Thailand : NORTHERN: Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Tak, Phitsanulok; NORTH-EASTERN: Phetchabun, Loei; EASTERN: Chaiyaphum, Nakhon Ratchasima; SOUTH-WESTERN: Kanchanaburi; CENTRAL: Nakhon Nayok; SOUTH-EASTERN: Chanthaburi; PENINSULAR: Yala.
Distribution : India, Burma, Indochina, Malaysia, Indonesia (type), Taiwan, Japan, New Guinea.
Ecology : Tropical evergreen rain forests, lower montane rain forests, mixed deciduous forests, on granite to limestone bedrock.
Vernacular : Ko dueai (ก่อเดือย), ko nam (ก่อหนาม), ko laem (ก่อแหลม)(Northern); ko it (ก่ออิด), ko mat (ก่อหมัด), ko daeng (ก่อแดง)(Northeastern); ko kin nuai (ก่อกินหน่วย)(Eastern).
Uses: Nuts edible, a pioneer species for forest plantation.