e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 7 > Part 4 > Year 2002 > Page 901 > Myrtaceae > Syzygium
76. Syzygium syzygioides (Miq.) Merr. & L.M.Perrywfo-0000319503
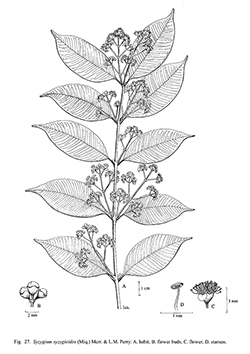
J. Arnold Arbor. 19: 109. 1938; in Mem. Amer. Acad. Arts 18: 171. 1939; Backer & Bakh.f., Fl. Java 1: 341. 1963; Chantar. & J.Parn., Thai Forest Bull. (Bot.) 21: 111. 1994; Turner, Gard. Bull. Singapore 47: 383. 1995.— Jambosa syzygioides Miq., Fl. Ind. Bat., 1: 431. 1855; N.P.Balakr., Fl. Jowai 1: 200. 1981; Harid. & R.R. Rao, Forest Fl. Meghalaya: 402, 1985.— Syzygium syzygiodes (Miq.) Amsh.; P.H.Hó, Câyco Viêtnam 2: 74. 1992.- Eugenia syzygioides (Miq.) M.R.Hend., Gard. Bull. Singapore 12: 154, figs. 30b & c. 1949; Kochummen in Ng, Tree Fl. Mal. 3: 219. 1978. Fig. 27.
Accepted Name : This is currently accepted.
Synonyms & Citations :
Description : Tree to 30 m. Twigs terete, the bark greenish brown or reddish brown. Leaves with petiole 4.2–7.7 mm, lamina 4, 5–8.7 by 1.9–3.8 cm, lanceolate, oblong lanceolate or ovate elliptic, base cuneate, apex acuminate or caudate-acuminate; midrib impressed on the upper surface, secondary veins 18–27 pairs, intramarginal vein 1. Inflorescence up to 7.5 cm, both terminal and axillary, paniculate; peduncle up to 10 mm, rachis and branches compressed; bracts 0.5 by 0.3 mm, triangular; bracteoles 0.5–0.6 by 0.4 mm, triangular. Flowers white, sessile. Hypanthial cup 3.1–4.2 mm, funnel-shaped. Pseudostipe 1.3–1.7 mm. Sepals 4, 0.5–0.8 mm, triangular. Petals 4, 1.5–2.6 mm, free, orbicular, membranous, 20–25 gland dots per petal. Outer stamens 3.5–5.4 mm; anther 0.4 mm, ovate. Style 2.9–6.1 mm. Ovary 2 locular, 5–10 ovules per locule. Fruits (immature) globose.
Thailand : NORTH-EASTERN: Nong Khai; EASTERN: Nakhon Ratchasima; SOUTH WESTERN: Kanchanaburi, Phetchaburi, Prachuap Khiri Khan; SOUTH-EASTERN: Prachin Buri, Chanthaburi; PENINSULAR: Chumphon, Ranong, Surat Thani, Phangnga, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Trang, Songkhla, Yala, Narathiwat.
Distribution : Andaman Islands, Assam, Burma, Indochina, Malesia.
Ecology : Streamsides, evergreen and secondary forests, beaches.
Vernacular : Wa san (หว้าซั้น), wa hak yong (หว้าฮากยอง)(Nong Khai); daeng khi nok (แดงขี้นก), daeng dong (แดงดง)(Prachuap Khiri Khan); wa som (หว้าส้ม)(Chon Buri); daeng khlong (แดงคลอง)(Chumphon); met chun (เหม็ดชุน)(Nakhon Si Thammarat).
Uses: Timber. Bark for dying or tanning. Fruits are edible.
Notes: In habit Syzygium syzygioides is very like S. urophyllum but differs in, amongst other features, its more conspicuous and numerous secondary veins.