e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 7 > Part 3 > Year 2001 > Page 401 > Hamamelidaceae > Altingia
Altingia excelsa Noronhawfo-0000529089
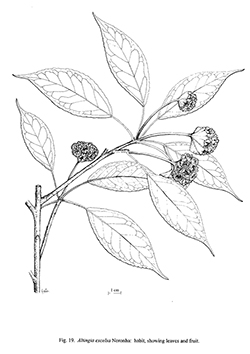
Verh. Genootsch. Kiinster 5, art. 2: 1. 1790; Kurz, Fl. Burm. 1: 445. 1877; C.B.Clarke in Fl. Brit. Ind. 2: 429. 1878; Brandis, Ind. Trees: 302. 1906; Vink in Fl. Mal. I, 5: 376, 1957; Phengklai, Thai For. Bull. (Bot.) 15: 3. 1985. Fig. 19.
Accepted Name : Liquidambar excelsa (Noronha) Oken
Allg. Naturgesch. 3(3): 1539. 1841.
Synonyms & Citations :
Description : Evergreen tree, 20–40 m high, usually with straight bole; bark grey to brownish grey, narrowly longitudinally fissured, and peeling off in thin, long, irregular flakes; twigs glabrous with permanent leaf scars; buds ovoid. Leaves elliptic to ovate-lanceolate, 6–12 x 2–5 cm, apex acute to acuminate, base obtuse, rounded or slightly cuneate, pustulate, usually curved upwards, dark, glandular-dotted at crenate or serrate margin, secondary nerves 5–10 pairs, anastomosing. Petiole 1–3 cm long, glabrescent. Male flowers in spikes or racemes, 5–10 cm long, reflexed, with 6–14 flowers. Stamens glabrous, up to 2 mm long. Female flowers in a globose head, ca 1 x 1 cm with 4–18 flowers; peduncle 2–3 cm, pubescent. Ovary ¾ inferior; styles recurved and sulcate, 3–4 mm long. Capsules united into a woody, globose or pyramidal head, ca 1.5 diam, with 4–18 capsules, each capsule up to 1 cm long with one fertile seed; fruiting peduncle 2–3.5 cm. Seed winged.
Thailand : NORTHERN: Chiang Rai, Phitsanulok; EASTERN: Chaiyaphum, Nakhon Ratchasima.
Distribution : India (type), Burma, China, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Malay Peninsula, Malesia.
Ecology : Near streams in evergreen forests, 600–800 m alt. Flowering and fruiting: November–February.
Vernacular : Hom (หอม), kratuk (กระตุก), nut (นูด), prok (ปรก), satue (สะตือ), sop (สบ), tamyan (ตำยาน), yan (ยาน)(Northern, Eastern).
Uses: Young leaves eaten as vegetable. The aromatic resin used for chemical and aromatic purposes. Wood good for indoor construction and cabinet work.