e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 7 > Part 1 > Year 1999 > Page 246 > Sapindaceae > Xerospermum
2. Xerospermum noronhianum (Blume) Blumewfo-0000428410
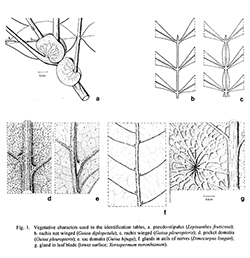
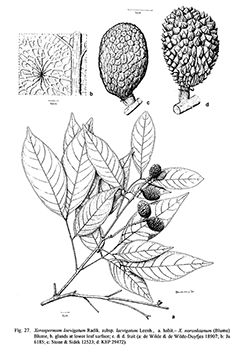
Rumphia 3: 100. 1847; Radlk. in Engl., Pflanzenr. 98: 946. 1932; Leenh., Blumea 28: 394, f. lc, 2a–c, e. 1983 (see also for complete synonymy); Yap in Tree Fl. Mal. 4: 461. 1989; Leenh. in Fl. Males., Ser. 1, Spermat. 11: 750, fig. 84b–e. 1994.— Euphoria noronhiana Blume, Bijdr. 234. 1825, comb. illeg. Fig. 1g, 27b–d; Plate VIII: 3.
Accepted Name : This is currently accepted.
Synonyms & Citations :
Description : Trees up to 25(–40) m high; bark black to brown to greyish, smooth, lenticellate or with large flakes. Leaves 1–2(–3)-jugate. Leaflets elliptic, up to 50 by 30 cm, coriaceous; base obtuse to acute; apex rounded to acuminate; (sub)glabrous on both sides. Inflorescences up to 25 cm long, but much shorter when tufted. Flowers white to yellow, small, scented. Sepals 4, ovate to obovate, 1–2(–3) by 1–2.4 mm, petaloid. Petals 4, obovate to broadly spathulate, 1–2.8 by 0.5–1.7 mm, short- to long-clawed. Stamens 8 (9); filaments 1.5–2.5 mm long, light green; anthers 0.3–0.8 mm long, dark purple. Fruits turning from yellow to red or dark brown; pedicel very swollen, (3.5–)5–7 mm thick; lobes subglobular to ellipsoid, 1.8–5 by 1.25–5 cm, aculeate to tuberculate; wall coriaceous, thin to 2.5 mm thick. Seeds: sarcotesta yellow.
Thailand : NORTHERN: Mae Hong Son; SOUTH-EASTERN: Nakhon Ratchasima, Chon Buri, Rayong, Chanthaburi, Trat; PENINSULAR: Chumphon, Ranong, Surat Thani, Phuket, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Trang, Satun, Narathiwat.
Distribution : Bangladesh, India (Assam), Burma, Indochina, Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Java (type), Borneo.
Ecology : Often common in primary and secondary evergreen forests, but also in peat swamp forests, beach forests, heath forests, or bamboo forests, on plains to slopes and crests, on dry to wet places, on a variety of soils, sea level up to 300( 1,500) m alt. Flowering throughout the year, but mainly in January–April; fruiting: mainly January–August. The fruits are eaten by birds and monkeys.
Vernacular : Kho laen (คอแลน); mak kho laen (หมักคอแลน)(Northern); kaem sang (แคมซาง), kha yao (ขะเหย้า), kho hia (คอเหี้ย), sa la man (สะละมาน)(Southeastern); cha luan (ช้าลวน), chet mon tan (เชตมอนตาล), kho laen khao (คอแลนเขา), laen ban (แลนบาน), mai ai dong (ไม้ไอ้ดง)(Peninsular).
Uses: The sarcotesta is edible. Reports of the quality of the wood are contradictory.