e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 5 > Part 4 > Year 1992 > Page 439 > Sonneratiaceae > Sonneratia
2. Sonneratia caseolaris (L.) Engl.wfo-0001140434
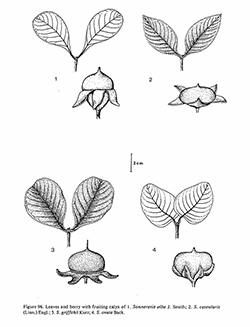
in Pflanzenfam. Nachtrag 1: 261. 1897; Craib in Fl. Siam. En. 1: 731. 1931; Back. & Steenis in Fl. Males., Ser. 1, Spermat.4: 283. F. 3c. 1951; Cuong in Fl. C.L.V. 4: 199. Pl. 1, 3 –4. 1965; Back. & Steenis in Fl. Males., Ser. 1, Spermat. 6: 973. F. 17, a–d. 1972; Whitmore in Tree Fl. Mal. 1: 445. 1972; Fl. Bangladesh 12: 6. 1980. Duke & Jackes, Blumea 32: 289. F. 4. 1987.— Rhizophora caseolaris L. in Herb. Amb.: 13. 1754, pro parte. Fig. 96: 2; Plate XXX: 46– 49.
Accepted Name : This is currently accepted.
Synonyms & Citations :
Description : Medium-sized, erect tree, 8–20 m high, evergreen; bark light brown, smooth to irregularly shallowly fissured. Pneumatophores long and slender, 50–100 cm long, pointed, often forked at terminal ends; bases 5–8 cm diam., much thicker in old tree. Leaves elliptic, elliptic-oblong, narrowly ovate or obovate, 6–10 by 2–5 cm; apex bluntly acute to shortly mucronate or obtuse; base cuneate; midrib sometimes reddish towards petiole; petioles 2–6 mm long. Flowers mostly 1 or 2. Calyx obovoid-terete in bud, 2–2.7 by 1.2–1.7 cm, apex acute; calyx-tube shallowly cup-shaped, ridged; calyx-lobes (5–)6–7, 1.4–2.2 cm long, inner surface tinged reddish-pink. Petals as many as calyx-lobes, 1.5–2.6 cm by 1–2 mm. Filaments 2.8–4 cm long, red in the flower part, white in the upper. Peduncle often tetragonous. Berry 2.5–3.5 cm high, 4–6 cm across; flat fruiting hypanthium 4.5–6.3 cm diam. including subhorizontally spreading calyx-lobes.
Thailand : Thailand. Hence, Sonneratia lanceolata is treated here as an ecotype of the widely distributed S. caseolaris.
Distribution : Sri Lanka, India, SE Asia, Malesia (Moluccas – type), N Australia, Solomon Islands, the New Hebrides.
Ecology : One of the common pioneer tree species in the mangrove forests, preferring less saline areas with deeply muddy soil, often colonizing tidal river banks where fresh water is frequent. The tree is also found sporadically as far as the inland limits of salinity.
Vernacular : Lam phu (ลำพู).
Notes: N.C. Duke and ER. Jackes (op. cit.) recognize Sonneratia lanceolata as a distinct species separable from S. caseolaris mainly on account of serveral variable characters (i.e. colour variation of staminal filaments, variable leaf shapes). The white staminal filaments, a main characteristic of S. lanceolata, for example, are occasionally encountered in the same population of S. caseolaris with the red and white staminal filaments, in the mangrove formations of Thailand. Hence, S. lanceolata is treated here as an ecotype of the widely distributed S. caseolaris.