e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 9 > Part 3 > Year 2008 > Page 211 > Fagaceae > Castanopsis
16. Castanopsis indica (Roxb.) A.DC.wfo-0000814085
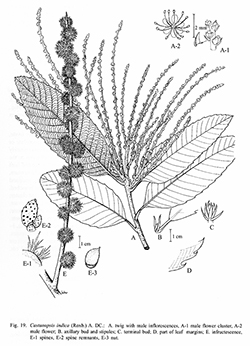
J. Bot. 1: 182. 1863; Prodr. 16.2: 109. 1864; King ex Hook.f., Fl. Brit. Ind. 5: 620. 1888; Craib, Bull. Misc. Inform. Kew 1911: 473. 1911; Contr. Flora Siam, Dicot.: 202. 1912; Hickel & A.Camus, Fl. Indo-Chine 5: 1027. 1930; Barnett, Quer. Rel. Fag. Asia: 159. 1940; Trans. & Proc. Bot. Soc. Edinburgh 34: 366. 1944; Hjelmq., Dansk Bot. Ark. 23.4: 495. 1968; C.C.Huang, Y.T.Chang & B.M.Bartol. in C.Y.Wu & P.H.Raven, Fl. China 4: 323. 1999.— Castanea indica Roxb. ex Lindl. in Wallich, Pl. Asiat. Rar. 2: 5. 1830; Fl. Ind. ed. 1832, 3: 643. 1832; Kurz, Forest Fl. Burma 2: 478. 1877.— Quercus indica (Roxb.) Drake, J. Bot. (Morot) 4: 153. 1890. Fig. 19.
Accepted Name : This is currently accepted.
Description : Tree, 7–30 m high, 50–250 cm girth. Terminal buds ovoid, 5–6 by 3–4 mm; bracts pubescent outside. Twigs tomentose then glabrescent, lenticellate. Bark brownish or greyish, thick scaly; inner bark yellowish; sapwood white. Leaves oblong, ovate or slightly obovate, 10–20 by 4–10 cm; base obtuse, equal or suboblique; apex acute, acuminate, sometimes obtuse; margins serrate in upper half to two-thirds; coriaceous, glabrous except along midrib above, densely pubescent below; midrib and nerves prominent below, more or less depressed above; lateral nerves 15–21 pairs, rather straight to the end of the serrate margins, scalariform veins fine but distinct below. Petiole 1.5–2 cm, pubescent then glabrescent. Inflorescences male and female separate or mixed, terminal and axillary, tomentose. Male inflorescence always branched, spikelets 10–15 cm long; bracts and bracteoles triangular, ca 1.5 by 1.5 mm, pubescent outside. Male flowers white, scented, solitary or in 2–3-flowered cluster; calyx 6-lobed, lobes obovate, free, ca 1 by 0.5 mm, pubescent outside; stamens 6–12, ca 2 mm long, glabrous; rudimentary ovary globose, flattened on top, ca 1 mm in diam., hirsute. Female inflorescence spike 8–25 cm long. Female flowers always solitary, not in clusters, other characters as in male flowers; styles 3, divergent, pilose at base; stigmata pointed, blackish. Fruits sessile, ovoid, 1.5–4 cm in diam. (including cupule), clustering by their spines in groups of 2–3 alternating with solitary fruit on an erect infructescence 15–30 cm long. Cupule completely enclosing the nut except the umbo; wall completely covered by tufted, erect, simple spines. Nut 1 per cupule, conical or ovoid, 1.3–1.5 by 0.8–1.1 cm, usually curved to one side; scar ca 1 cm in diam.; at base or rather above.
Thailand : NORTHERN: Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Nan, Lampang, Phitsanulok; NORTH-EASTERN: Phetchabun, Loei, Khon Kaen; EASTERN: Chaiyaphum.
Distribution : India, Nepal (type), Burma, China, Taiwan, Laos, Vietnam.
Ecology : Tropical evergreen rain forests, dry dipterocarp forests, moist upper mixed deciduous forests, open grasslands, 500–2,000 m (most commonly 500–900 m). Flowering: February–December (most commonly February–May); fruiting: February–December (most commonly May–July), usually flowering and fruiting at the same time.
Vernacular : Ko lim (ก่อลิ่ม), ko rang (ก่อหรั่ง), ko yum (ก่อหยุม), ko nam (ก่อหนาม), ko paen (ก่อแป้น)(Northeastern); ko khao (ก่อข้าว), ko ti (ก่อตี), ko daeng (ก่อแดง)(Northeastern).
Uses: Nuts edible.