e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 7 > Part 4 > Year 2002 > Page 801 > Myrtaceae > Melaleuca
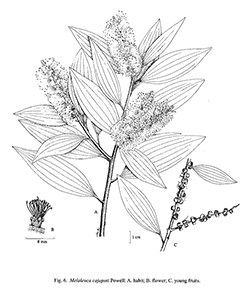
Melaleuca cajuputi Maton & Sm. ex R.Powell
Pharm. Lond. Trans.: 22. 1809; Kochummen in Ng, Tree Fl. Mal. 3: 248. 1978; P.H.Hô, Câyco Viêtnam 2: 73. 1992; Turner, Gard. Bull. Singapore 47: 370. 1995. Fig. 6; Plate XXVII: 4.
Accepted Name : This is currently accepted.
Synonyms & Citations :
Description : A large tree to 30 m or small shrub. Outer bark brown (white on twigs), often spongy, papery, soon peeling off in layers, inner bark pink, twigs light grey. Branches pendulous (tree) or upright (shrub). Leaves lanceolate, 5.5–15 by 1–3 cm, oblique or falcate, blunt to acute or acuminate, coriaceous, 3–7-ribbed, upper and lower surfaces drying green, both surfaces more or less glabrous when mature, sericeous when young. Petioles 2–4 mm, flattened, minutely sericeous. Flowers rarely solitary usually in clusters of three always forming interrupted spikes 6–17 cm long, the top of the spike apparently growing into a new leafy branch. Bracteoles lanceolate, sericeous, deciduous. Pedicels absent. Calyx ovoid 2 mm, sericeous and ciliate; lobes obtuse 0.5 mm often with a scarious margin. Pseudostipe absent. Petals white, 1.5–2 mm long. Stamens numerous, grouped in 5 antipetalous broadly based fascicles, usually containing about 7 stamens, longest filaments ca 10 mm, connective with a minute apical gland. Style up to 10 mm. Ovary inferior, top sericeous, stigma linear. Fruits 2–3 mm. Seeds straight or curved, ca 1 mm by <0.5 mm.
Thailand : SOUTH-EASTERN: Chon Buri, Rayong, Chanthaburi, Trat; PENINSULAR: Ranong, Surat Thani, Phangnga, Phuket, Nakhon Si Thamarat, Satun, Songkhla, Narathiwat.
Distribution : India, Burma, Cambodia, Vietnam, China, Malesia (Moluccas type), Australia.
Ecology : In various types of wet forests, usually at low altitudes on white sand. Often dominant in seasonally flooded forests where it may form almost monospecific stands.
Vernacular : Samet (เสม็ด); samet khao (เสม็ดขาว)(Eastern); met (เม็ด)(Peninsular).
CommonName : Cajeput tree, Paper bark tree, Swamp trea, Milk wood.
Uses: The essential oils (cajuput oil) are used medicinally, principally for skin complaints and as an anodyne (toothache) or as a sudorific and occasionally as a mosquito repellent. The oil can also cause dermatitis. The timber, which is very durable, is used for various construction purposes and as fuel. The bark is used as caulking and for torches.
Notes: True Melaleuca leucadendra (L.) L., a species thought to be fairly common in SEAsia, does occur in Malesia, but more rarely than previously thought, being largely confined to the Moluccas, New Guinea and Australia.