e-Flora of Thailand
Volume 6 > Part 3 > Year 1997 > Page 198 > Loganiaceae > Fagraea
1. Fagraea fragrans Roxb.wfo-0000685577
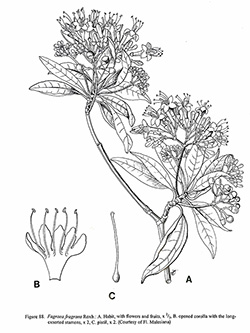
Fl. Ind. 2: 32. 1824; Kurz, Fl. Burm. 2: 205. 1877; Clarke in Fl. Br. Ind. 4: 85. 1883; Dop in Fl. Gén. I.-C. 4: 177. 1914; Corn., Ways. Trees. 1: 424–425. 1940; Kerr in Fl. Siam. En. 3: 35. 1951: Leenhouts in Fl. Males., Ser. 1, Spermat. 6: 304. Figs. 5–8. 1962; Tirel-Roudet in Fl. C.L. V. 13: 53. 1972; Whitmore, Tree Fl. Mal. 2: 273. 1972; Hô, Câyco Vietnam 2: 847. Fig. 6065. 1992. Figure. 88. Plate XVI 3.
Accepted Name : Cyrtophyllum fragrans (Roxb.) DC.
Prodr. 9: 31. 1845.
Synonyms & Citations :
Description : Tree 8–30 m, bark brown, deeply fissured, slash-mark yellowish-white; twigs greyish brown, ± terete. Leaves: petiole 0.7–2 cm, slender, terete, without auricles; lamina usually elliptic, less commonly oblong to ovate to obovate to oblanceolate, 7–1 1 by 3–4.2 cm; base acute to attenuate; apex acute, acuminate or caudate (acumen 0.2–1 cm); thinly coriaceous; main vein slightly raised above, prominently keeled or ridged below; secondary veins 5–9 pairs, barely visible and slightly sunken or invisible above, visible below. Stipules 1–2 mm high in leaf axils. Inflorescence 4–12 cm, axils of the uppermost leaves, lax to dense, 3-many flowered; peduncle 2–6.5 cm; pedicels 3–6 mm. Calyx 1.7–3 mm, campanulate; lobes 0.7–2 mm, apex rounded, spreading in fruit. Corolla 1.2–2 cm, creamy white turning salmon coloured or dull-yellow; tube 0.65–1.2 cm, narrowly funnel-shaped; lobes 5.5–8 mm, oblong. Stamens exserted well beyond the corolla, filaments 1.4–2.2 cm, anthers 1.5–2 mm, oblong to elliptic. Ovary and style 1.7–2.4 cm, stigma 0.7–1 mm, capitate or obconical, occasionally faintly bi-lobed. Fruit 4.5–8 mm, globose, green turning orange or red. Seeds 1–2 mm, roughly angled.
Thailand : NORTHERN: Nan, Lampang; NORTH-EASTERN: Nakhon Phanom; EASTERN: Surin, Ubon Ratchathani; SOUTH-EASTERN: Trat; PENINSULAR: Chumphon, Surat Thani, Trang, Satun, Narathiwat.
Distribution : Andaman Islands, N India, S Burma, Vietnam, Malesia (type: Malaysia).
Ecology : Evergreen forests, mixed deciduous forests, sandy sea-shores, by roadsides, often planted as an ornamental or for its timber.
Vernacular : Kankrao (กันเกรา)(Central); ta-ma-suu (ตะมะชู), tam-muu-suu (ตำมูซู)(Malay-Peninsular); ta-trao (ตะเตรา)(Khmer-Eastern); tamsao (ตำเสา), thamsao (ทำเสา)(Peninsular); man pla (มันปลา)(Northern, Northeastern).
Uses: The timber is hard and very durable. Decoctions of the bark are used as a febrifuge and from the leaves in the treatment of severe diarrhoea.
Notes: The flowers are particularly fragrant.